Delete Excel Worksheets using PowerShell
Problem
In this blog post, we will show you how to delete Excel worksheets using PowerShell.
As the context, our original Workbook contains worksheets as follows:
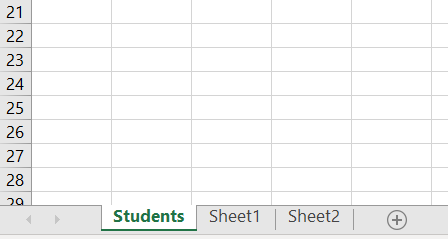
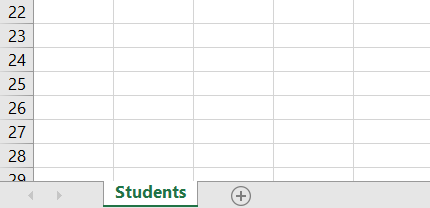
And we will delete worksheets other than Students worksheet that we feel unnecessary so that it will look as follows:
Using Excel Com Object
Since PowerShell is deeply integrated with .NET Framework, we can use ComObject to work with Excel files. After creating the object, we will open the Excel file and loop through all the worksheets. If worksheet’s name is not Students, we will delete it using Delete method from worksheet object.
try {
# Open excel file
$excel = New-Object -ComObject Excel.Application
$workbook = $excel.Workbooks.Open("C:\Scripts\Test.xlsx")
# Loop through all the worksheets and Delete worksheet other than "Students" worksheet
foreach ($worksheet in $workbook.Worksheets) {
if ($worksheet.Name -ne 'Students') {
$worksheet.Delete()
}
}
# Save excel file
$workbook.Save()
}
finally {
# Close excel file
$workbook.Close()
$excel.Quit()
[System.Runtime.Interopservices.Marshal]::ReleaseComObject($excel)
}
We enclose the code above with try-finally block because we want to make sure it will release the resource after modifying Excel that is performed at finally block.
Using ImportExcel Module
ImportExcel is an external module that is built based on EPPlus which is a very well-known library to work with Excel spreadsheets in .NET.
Before using ImportExcel module, we have to install it.
Install-Module -Name ImportExcel
And then following previous solution pattern, we have to create Excel object first before removing the worksheets. We will perform deletion using Delete method of Worksheets collection object.
try {
# Import the module
Import-Module ImportExcel
# Open excel file
$excel = Open-ExcelPackage -Path "C:\Scripts\Test.xlsx"
# Get all the worksheets
$worksheets = $excel.Workbook.Worksheets
# Loop through all the worksheets and Delete worksheet other than "Students" worksheet
foreach ($worksheet in $worksheets) {
if ($worksheet.Name -ne 'Students') {
$worksheets.Delete($worksheet)
}
}
}
finally {
# Close excel file
Close-ExcelPackage $excel
}
Similar to previous solution, we enclose the script with try-finally block to avoid memory leak.
Using PSExcel Module
PSExcel is another module based on EPPlus library. You can find all the examples in github repository.
Before using this module, we have to install it.
Install-Module -Name PSExcel
In order to use the object, we must import the module first. Then, we create Excel object by specifying the path of our Excel file. This object will be used to get all the worksheets that will be iterated. If worksheet’s name is not Students, then it will be removed using Delete method of Worksheets collection object.
try {
# Import the module
Import-Module PSExcel
# Open excel file
$excel = New-Excel -Path 'C:\Scripts\Test.xlsx'
# Get all the worksheets
$worksheets = $excel.Workbook.Worksheets
# Loop through all the worksheets and Delete worksheet other than "Students" worksheet
foreach ($worksheet in $worksheets) {
if ($worksheet.Name -ne 'Students') {
$worksheets.Delete($worksheet)
}
}
# Save excel file
$excel | Save-Excel
}
finally {
$excel | Close-Excel
}
We also enclose the script with try-finally block to avoid memory leak.
Conclusion
To remove Excel worksheets using PowerShell, we can use Excel Com Object which is based on .NET Framework. We can also use PowerShell external modules like PSExcel and ImportExcel. ImportExcel is an excellent module which is based on EPPlus library, a well-known C# libary for woking with Excel from .NET.
PSExcel is the alternative of ImportExcel module. PSExcel is also based on EPPlus but this module is no longer maintained as stated in its GitHub repository. If it doesn’t provide functionality that you need, you should contribute to the source code by yourself.