How to Zip and Unzip Files using PowerShell
Introduction
One common tasks often faced by System Administrators and Software Engineers is compressing and decompressing files or sometimes also known as archiving (zipping) and extracting (unzipping) files.
In this article we will explore how you can zip and unzip files using PowerShell.
How to Zip Files Using PowerShell
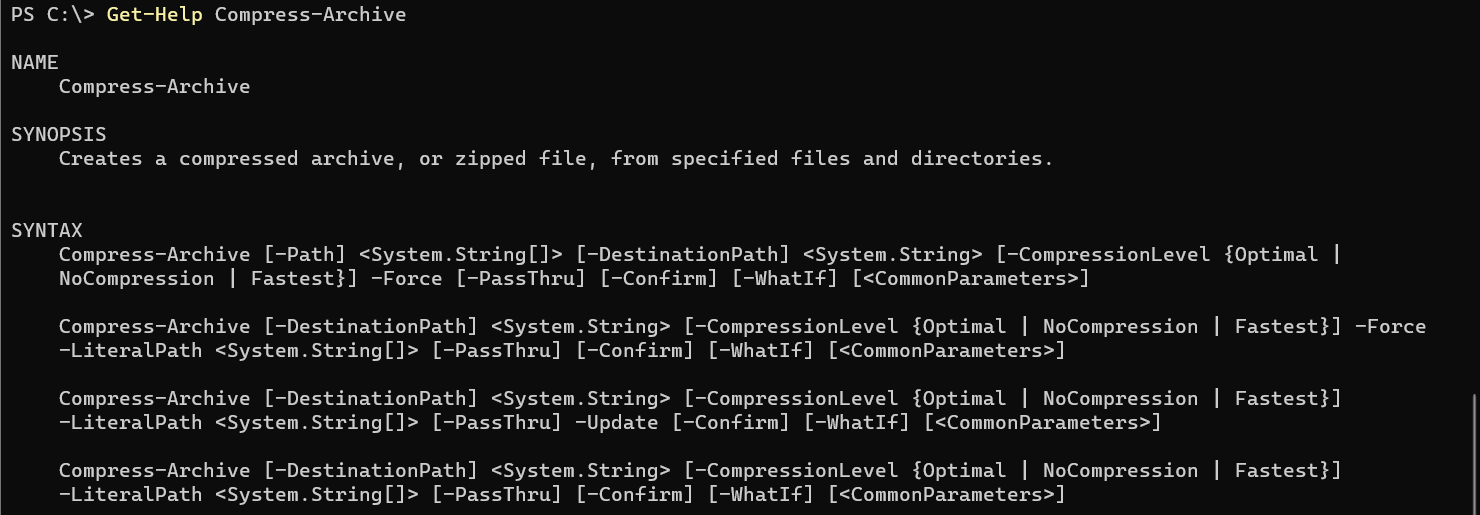
To zip files using PowerShell, we can use Compress-Archive cmdlet. It has several syntaxes that can be found using Get-Help Compress-Archive command.
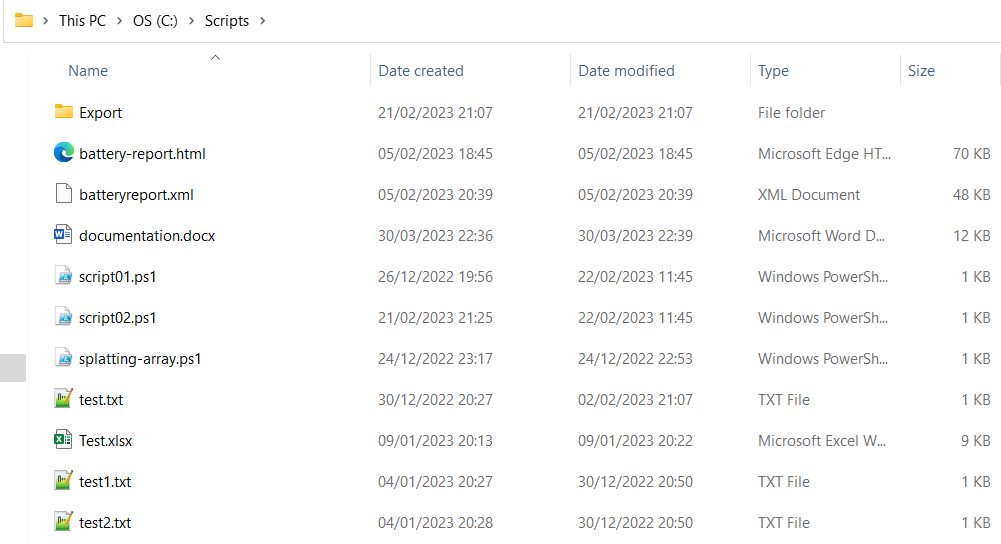
In this context, we have following directory structures containing a folder and some files. We will perform files compression based on this directory.
Compress specific files
To compress specific files, we can use Compress-Archive together with Path or LiteralPath parameter, then specify the files we want to compress.
Compress-Archive -Path 'C:\Scripts\test.txt', 'C:\Scripts\documentation.docx' -DestinationPath 'C:\Archives\Docs.zip'
Compress-Archive -LiteralPath 'C:\Scripts\test.txt', 'C:\Scripts\documentation.docx' -DestinationPath 'C:\Archives\Docs.zip'
Compress only specific file type
To compress only files with specific extension or file type, we can use Compress-Archive together with Path parameter then using asterisk * as wildcard. Wildcard can only be used with Path parameter, not LiteralPath.
Compress-Archive -Path 'C:\Scripts\*.txt', 'C:\Scripts\*.docx' -DestinationPath 'C:\Archives\Docs.zip'
Compress a directory and its subfolders and files
To compress a directory and its subfolders and files, we can use Compress-Archive with Path parameter, then specify the directory.
Compress-Archive -Path 'C:\Scripts\' -DestinationPath 'C:\Archives\Scripts.zip'
Compress a directory without its root folder
Similar to previous example, but we can exclude root folder from zip files. This means the compression result will only contain subfolders and files without the root folder.
Compress-Archive -Path 'C:\Scripts\*' -DestinationPath 'C:\Archives\Scripts.zip'
There are many more examples that can be found here.
How to Unzip Files Using PowerShell
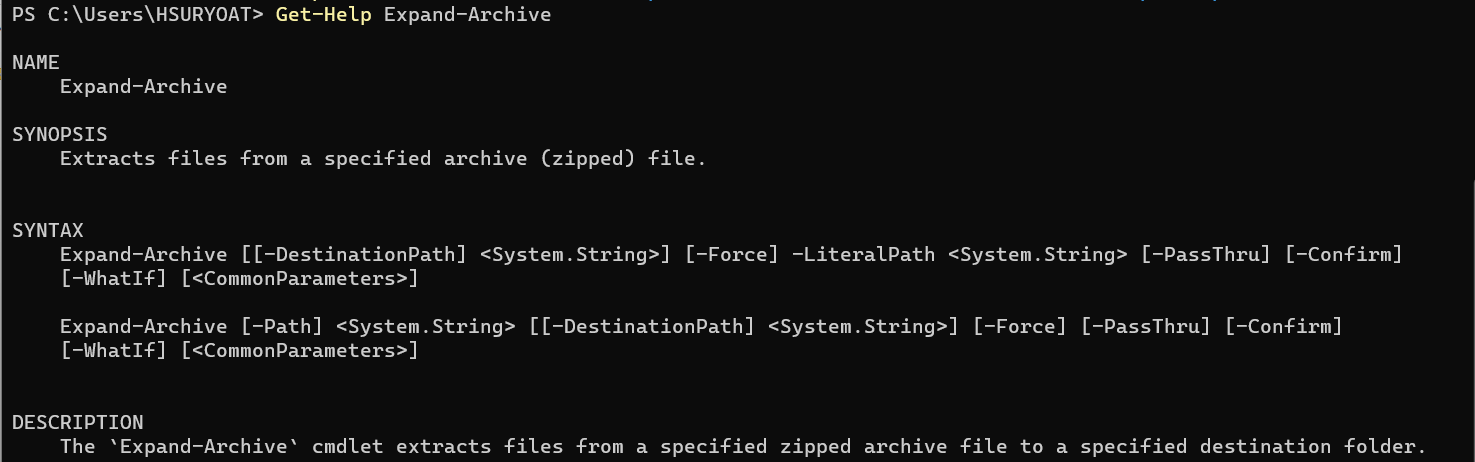
To unzip or extract files, we can use Expand-Archive cmdlet with its parameters. It has several syntaxes that can be found using Get-Help Expand-Archive command.
Extract zip file
To extract zip file, we need to use Expand-Archive cmdlet together with LiteralPath or Path parameter to specify the zip file we want to extract. We must also specify DestinationPath parameter to denote where the zip file will be extracted.
Expand-Archive -LiteralPath 'C:\Archives\Scripts.zip' -DestinationPath 'C:\Docs\'
If the zip file is located in current folder, we just need to specify the zip file using LiteralPath or Path parameter and set DestinationPath parameter value.
Expand-Archive -LiteralPath '.\Scripts.zip' -DestinationPath 'C:\Docs\'
Conclusion
To compress files we can use Compress-Archive cmdlet and specify the source files that will be compressed as well as the destination of zip file.
On the other hand, to extract the files we can use Expand-Archive cmdlet and specify the zip file we want to extract as well as the location of extracted file.